Connective Tissue Types Of Cartilage | All connective tissue types within the human body are derived from the embryonal mesoderm. Connective tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Dense regular connective tissue, cartilage, bone, adipose tissue, blood, and hematopoietic tissue. The different types of connective tissues, specialized (bone and cartilage), dense (tendon) and irregular connective tissues are depicted in three mouse e14.5 embryos. They are a loose array of random fibers that has a wide variety of cell type. Hyaline cartilage develops, like other types of connective tissue, from mesenchymal cells. Cartilage is a type of connective tissue found in the body. All connective tissue types within the human body are derived from the embryonal mesoderm. This is a grab bag category of diverse tissue types. General biology | getting started | cells | genetics | classification | evolution | tissues & systems | additional material. Other types of connective tissue include tendon and cartilage. It serves to connect and support other tissues and also has regulatory and immunologic the specific composition of the ecm determines the biochemical properties of the connective tissue. The types of connective tissue include cartilage, bone, collagen fibers, reticular fibers, elastic fibers, blood, hemopoietic/lymphatic, adipose tissue, bone marrow, and lymphoid tissue. Tissue that connects your body's muscles, organs, blood vessels, nerves and other parts to one another. Connective tissue is the most diverse and abundant tissue type. Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue that differs from bone in several ways; Each connective tissue acts to support and hold your body together and, in some instances, transmit substances. Connective tissues are the major supporting tissue of the body. There are many different types of. Cartilage is a form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is abundant and of a firmly gelated consistency that endows this tissue with unusual rigidity and resistance to compression. They are the elastic cartilage, hyline cartilage, and fibrous cartilage. Cartilage is a unique tissue type because it doesn't have blood vessels or nerves. In addition, they nourish and pillows epithelia. Connective tissues perform many functions in the body, but most importantly, they support and connect other tissues; These support the body, protect the various organs and help this type of cartilage is found in the pinna and external auditory canal of the ear, eustachian tubes, epiglottis and tip of the nose. Cartilage is a unique tissue type because it doesn't have blood vessels or nerves. Connective tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Cartilage is a type of connective tissue found in the body. Dense regular connective tissue, cartilage, bone, adipose tissue, blood, and hematopoietic tissue. There are many different types of. All connective tissue types within the human body are derived from the embryonal mesoderm. General biology | getting started | cells | genetics | classification | evolution | tissues & systems | additional material. Cartilage is a connective tissue consisting of a dense matrix of collagen fibres and elastic fibres embedded in a rubbery ground substance. Cartilage resists compression and covers the type i collagen forms fibers and is found in most connective tissues with bone, ligaments, tendon and skin having the high concentrations of type i. Cartilage is a type of connective tissue found in the body. Hyaline cartilage develops, like other types of connective tissue, from mesenchymal cells. Cartilage is a unique tissue type because it doesn't have blood vessels or nerves. Connective tissues most associated with running include bone, tendons, ligaments, cartilage and fascia. Specialized connective tissue types include: The different types of connective tissues, specialized (bone and cartilage), dense (tendon) and irregular connective tissues are depicted in three mouse e14.5 embryos. Provides support in areas of heavy pressure. Connective tissue is the most abundant type of tissue in the body. They are a loose array of random fibers that has a wide variety of cell type. Blend of hyaline cartilage and dense connective tissue; Specialized connective tissue types include: Cartilage is a connective tissue consisting of a dense matrix of collagen fibres and elastic fibres embedded in a rubbery ground substance. There are many different types of. Connective tissue is the tissue that connects, separates and supports all other types of tissues in the body. They are the elastic cartilage, hyline cartilage, and fibrous cartilage. Proper, which covered dense connective tissue is divided into regular and irregular types. It form inter cellular substance between cells of different types of tissue, so that help in friction less movement of the body organ. When an embryo is developing, cartilage is the precursor to bone. Provides support in areas of heavy pressure. These connective tissues form the endoskeleton of the vertebrates. Cartilage is a unique tissue type because it doesn't have blood vessels or nerves. In addition, they nourish and pillows epithelia. With the exception of cartilage, all connective tissues are. Cartilage connective tissue has limited ground substance and can range from semisolid to a flexible matrix. Cartilage resists compression and covers the type i collagen forms fibers and is found in most connective tissues with bone, ligaments, tendon and skin having the high concentrations of type i.
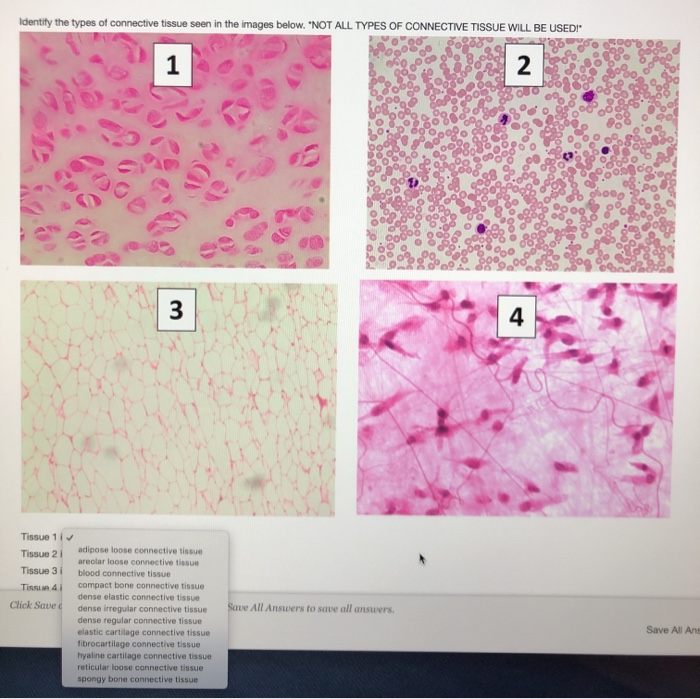

Each connective tissue acts to support and hold your body together and, in some instances, transmit substances connective tissue types. Specialized connective tissue types include:
Connective Tissue Types Of Cartilage: Connective tissue is the most abundant type of tissue in the body.
0 Tanggapan:
Post a Comment